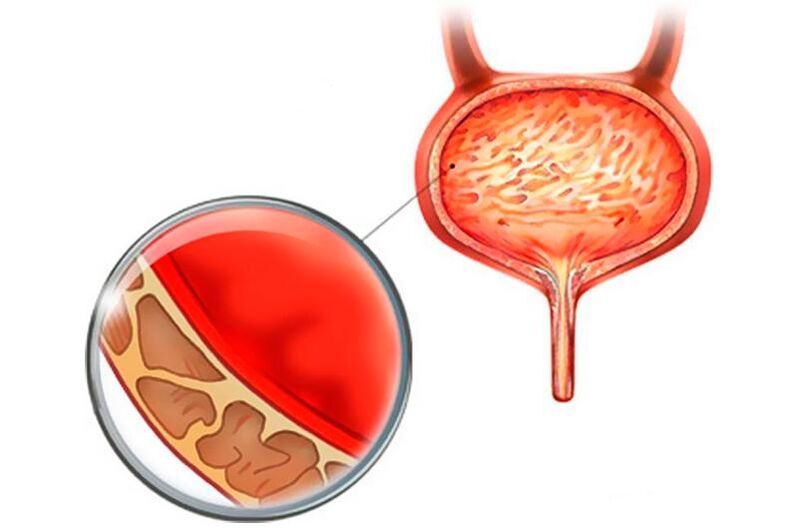
Cystitis is an inflammation of the bladder walls. In practical urological terminology, the word "cystitis" is usually used to denote a symptomatic infection of the urinary tract, with manifestations of inflammation of the bladder mucosa, impaired functionality and changes in the urine sediment.
The signs of cystitis appear suddenly:
- frequent urination (every 15-20 minutes);
- sharp pain during urination in small doses;
- impurity of blood in the urine (sometimes);
- low-grade fever.
If not treated immediately, cystitis can become chronic or the infection can travel through the kidneys (renal disease) or down the urethra (urethral disease).
According to statistical expertise, women aged 14 to 60 had cystitis at least once in their lives, especially sexually active women aged 20-50 who had diabetes mellitus and a history of reduced immune system functions.
Modern children, as practice shows, quite often suffer from cystitis, even babies and infants. It is sad that many parents cannot predict the development of this disease in a child.
Cystitis, based on the nature of the process, occurs:
- acute: appears suddenly, accompanied by local (frequent and painful urination) and general symptoms (fever, general weakness);
- chronic: found in laboratory tests, symptoms are slow or absent, but during exacerbation occurs in the form of acute.
Based on the causative agent, cystitis also occurs:
- non-specific: against the background of conditionally pathogenic microflora (enterobacteria, candida, staphylococci, proteus, klebsiella);
- specific: due to sexually transmitted diseases (chlamydia, ureaplasmosis, syphilis) or renal tuberculosis.
Causes of cystitis
Most episodes of the disease show that the main cause of cystitis is infection by representatives of the conditionally pathogenic environment of the human body - staphylococci, streptococci, Escherichia coli, as well as infection with genital ureaplasma and mycoplasma infections.
Today it is known that cystitis, the causes of which are quite clear, cannot be caused by only one factor.
The complex of factors leading to the appearance of cystitis:
- Indiscriminate intercourse: the close proximity of the urethral opening to the vagina contributes to easy contamination during intercourse with both female and male flora.
- Failure to follow the rules of intimate hygiene such as daily washing of the external genitalia, frequent change of sanitary napkins and underwear during menstruation, washing of the genitals after sexual intercourse, keeping clean underwear, using daily sanitary napkins.
- Chronic dysbacteriosis or vaginal candidiasis: the disturbed intestinal and / or vaginal microflora sometimes contributes to the growth of the population of conditionally pathogenic microflora, after which the microflora, unusual for the genital and urinary systems, causes an inflammatory process, damaging the entire organism.
- Dysfunctions of the immune system: a decrease in immune protection or allergic local pathologies significantly reduce the body's resistance to diseases, which gives carte blanche to pathogenic bacteria to easily enter the bladder cavity.
- Infrequent urination: a woman's bladder can accumulate 250-500 ml of urine inside, and its regular untimely emptying leads to structural changes in the bladder, sphincter and creating greenhouse conditions for infection and reproduction of pathogenic microorganisms.
- The decrease in defense forces leads to the fact that the infection freely penetrates up into the cavity of the bladder and provokes an inflammatory process in it.
- The presence of Escherichia coli E. coli (in 70-95% of patients).
- The presence of Staphylococcus aureus (Staphylococcus saprophyticus) in 5-20% of patients.
- Presence of Klebsiella spp and Proteusmirabilis (Proteus) in other patients.
- Bladder catheterization in men and women: sometimes leads to urethral infection. This procedure is particularly dangerous for pregnant women and women in labor, especially in the postoperative period, when the tone of the urinary tract is reduced and gram-negative bacteria have shown activity.
- The content in the body of various fungi (Candida and others), chlamydia, Trichomonas, mycoplasmas and viruses.
Cystitis in an acute form, a woman can get sick several times, and the disease often becomes chronic.
In men, cystitis develops rarely, as a rule, after inflammation of the urethra, prostate gland, epididymis and seminal vesicles. The possibility of developing cystitis increases with bladder catheterization in men suffering from prostate adenoma, one of the symptoms of which is constant retention of urine.
Symptoms of cystitis
Cystitis is a very unpleasant, painful disease that delivers many uncomfortable and painful sensations to a sick person, which they often bravely endure, not realizing the dangers that can subsequently cause complications from untreated cystitis. As a rule, acute cystitis appears suddenly, and cystitis after intercourse occurs after 8-10 hours.
The symptoms of cystitis are very painful, the most characteristic of them:
- cutting pains during urination;
- burning and cutting at the end of the act of urination;
- protracted pains in the lower abdomen, sometimes unbearable;
- a feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder;
- sometimes urinary incontinence with a strong urge to urinate (more often in children);
- cloudy or bloody (hematuria) urine;
- sometimes a slight increase in body temperature with slight chills.
An increase in temperature during cystitis can also signal a possible inflammation in the kidneys or somewhere else, so immediate referral to a specialist would be a very wise course of action.
It is known that women and girls suffer from cystitis much more often than men and boys. Oddly enough, the probability of cystitis during pregnancy increases significantly, although during this period any disease is highly undesirable. Quite often, cystitis develops in the early stages of pregnancy, sometimes even before the woman knows about it. In addition to everything else, cystitis is often called a non-specific or relative sign of pregnancy.
Cystitis in early pregnancy manifests itself with the following symptoms:
- varied pain, which can vary from moderate pain in the lower abdomen with slight soreness at the end of urination to sharp, cutting pain with urinary incontinence;
- frequent urge to urinate with a small amount of urine;
- urine may have a strong smell, dark color;
- constant pain in the lumbar region;
- mild hematuria (not always);
- cod (optional)
- menstrual disorders in women of childbearing age.
In the elderly and children, the symptoms of cystitis are often not as obvious. Fever, abdominal pain, and nausea may be the only symptoms of cystitis.
In a disease like cystitis, the symptoms and treatment are always completely dependent on the patient's sense of responsibility for his health.
Spread of cystitis
Acute cystitis is one of the most common diseases in urology. Most often, uncomplicated cystitis is observed when the bacteria affect only the mucosa of the bladder, leaving the submucosal layer intact.
According to scientific and statistical research in urological practice, the prevalence of cystitis among women is 500-700 episodes per 1000 patients, and among men aged 21 to 50 - only 6-8 cases per 1000, and the acute form of cystitis in men isobserved extremely rarely.
The higher prevalence of cystitis among women is explained by factors:
- the female urethra (urethra) is shorter and its lumen is wider than that of the male urethra;
- the external opening of the urinary canal of women goes directly to the perineum, which contributes to the easy penetration of infection from the genital tract;
- the external opening of the urethra is located near the anus, which contributes to the development of 80% of cystitis from infection with intestinal bacteria (E. Coli) that entered the bladder from the intestinal lumen.
The incidence of cystitis in girls is three to four times higher than the incidence in boys. In newborns and children under 1 year, cystitis is extremely rare, the disease is more often detected at the age of 1 to 3 years and in adolescence (13-15 years), but children from 4 to 12 years of age are most often affected.
cystitis in summer
Oddly enough, but during the warm summer season, especially during the holidays, when most women go on vacation to other climatic zones, cases of cystitis become more frequent for reasons:
- holiday accommodation with the impossibility of high-quality hygienic care for intimate areas;
- hypothermia of the body after too long a bath in a cold tank;
- failures in the usual mode of urination (flight, moving, new place) when you have to hold for a long time;
- a sudden change in the climatic zone, causing a decrease in the functions of the immune system;
- often increased sexual activity at rest and so on.
You should urgently contact a urologist if suddenly you cannot avoid cystitis while resting at the resort. Clarifying the diagnosis, take a urine test and undergo an ultrasound scan.
The latest antibacterial drugs and antibiotics will effectively speed up your recovery and prevent complications (transition of acute cystitis into chronic). The fact is that they act exclusively on the inflammatory process in the bladder, almost without affecting the other organs and systems of the body, concentrating as much as possible in the urine and the diseased mucous membrane of the bladder. The toxicological effect on the body is minimal.
Particularly successful in the treatment of cystitis in the summer is taking a drug from the fosfomycin group, which does not have phototoxicity, like other drugs of the same series. The drug, which does not contain components with photosensitizing and photoreactive properties, does not increase the sensitivity of the skin to the ultraviolet radiation of the sun even at low intensity, therefore it does not cause redness and burns of the skin, which means that it can be taken without disturbingbeach mode.
The phosphonic acid derivative also has an almost complete lack of side effects, which makes it possible to effectively and safely treat cystitis in children and pregnant women, taking it once for uncomplicated acute cystitis. Chronic and other, more serious forms of cystitis will also be successfully treated with this medicine, but the medicine will be taken according to a certain schedule.
When you go on a long-awaited summer vacation, it will not be superfluous to fill your first aid kit with a broad-spectrum antibiotic just in case.
cystitis during pregnancy
The inflammatory process in the bladder can begin in a woman at any stage of pregnancy. In any case, cystitis during pregnancy will be considered complicated and therapy should be carried out exclusively under inpatient medical supervision.
The main causes of cystitis during pregnancy:
- hemodynamic disorders;
- mechanical effects of the enlarged uterus on the displaced internal organs of the pelvis;
- hormonal imbalance.
All of these causes can make it difficult to empty the bladder, leading to chronic bladder retention and infection. At the first suspicion of cystitis, a pregnant woman should immediately contact a leading specialist who, if necessary, will refer her to a urologist.
Children's cystitis
Children's cystitis affects the younger generation at any age, but girls of preschool and school age - five to six times more often, and the main reasons for this are:
- the lack of ability of the ovaries of girls to produce estrogens;
- low barrier capacity of mucous membranes and skin;
- a short and wide urethra is "open" for the passage of pathogenic microorganisms into the bladder;
- irregular or insufficient hygienic care of the genitals;
- concomitant diseases that contribute to a decrease in the immune defense of the body.
The complex of these factors contributes to the creation of favorable conditions for the reproduction of pathogenic bacteria in the urethra and bladder.
Diagnosis of cystitis
Before starting treatment, it is important to reveal all the factors that led to the development of cystitis. Reliable diagnostics will help prescribe adequate therapy and give medical recommendations to avoid future relapses of the disease and prevent cystitis from becoming chronic.
The following tests will help the urologist make the correct diagnosis:
- doctor's examination and examination;
- overt symptoms;
- laboratory tests of urine and blood;
- bacteriological examinations of urine and smear from the urethra;
- carrying out special tests for the presence of nitrites and leukocytes in the urine;
- Bladder ultrasound;
- determining the presence of concomitant diseases.
If necessary, other methods of urological examination are also used.
Treatment of cystitis
How to treat cystitis? The speed and quality of the treatment of cystitis, the regeneration of the bladder mucosa always depend on the timeliness of the diagnosis and the well-chosen tactics of the complex treatment of the disease.
The choice of antibacterial drugs for the course of treatment of cystitis is determined by the following parameters:
- the duration of the illness;
- severity of symptoms;
- the presence of concomitant factors and pathologies;
- side effects of drugs, their absorption, way, speed of their release from the body, etc.
The effectiveness of the drug for the treatment of cystitis lies in the strength of its suggestiveness to one or another microorganism. It should be noted that pathogenic bacteria mutate and become insensitive to antibiotics. Decades ago, cystitis was treated very successfully with many bactericidal drugs. However, today one of the main causes of cystitis - E. coli - has become resistant to the effects of these drugs. In addition, the previous generation of antibiotics had a very high level of toxicity and many negative side effects.
When choosing a drug against pathogens of cystitis, the cost of treatment should also be taken into account, which will be expressed not so much in the price of the drug itself, but in its effectiveness, long-term use and existing risk to the patient's health.
Modern drugs for the treatment of cystitis selectively act on pathogens, concentrating in the bladder, thereby increasing their effectiveness. The use of antibiotics of the latest generation reduces the time of treatment of cystitis, reduces the risk of side effects, which causes less harm to the health of patients. A broad-spectrum antibiotic from the fosfomycin group, as an effective and safe drug, is used to treat cystitis in both pregnant women and children.
How to treat cystitis? In addition to antibiotic treatment, we must not forget other treatment methods:
- anti-inflammatory and analgesic therapy with antispasmodics;
- stimulation and modulation of the immune system;
- a diet without fatty and spicy foods;
- increased drinking regime;
- fear of hypothermia;
- a warm heating pad in the lower abdomen;
- exclusion of anxiety, stressful situations;
- active lifestyle;
- phytotherapy;
- using iontophoresis, UHF or inductothermy.
Remember that the presence of some gynecological diseases prohibits the use of physiotherapy and thermal procedures.
Useful tips to prevent cystitis
To prevent and prevent the occurrence of cystitis and its recurrence, follow simple recommendations:
- Follow the rules of personal intimate hygiene: wash your face at least once a day, preferably 2 or more times, using baby soap (without harmful additives) and running water.
- Observe your sexual partner for simple genital hygiene.
- Before and after each sexual contact, remember to wash with soap and your sexual partner should do this too.
- Exclude oral sex in the presence of stomatitis, tonsillitis, candidiasis and other infections of the oral cavity to avoid infection of the external genitalia and urethra through saliva.
- Wear clothes according to the weather, not according to fashion. Payback for a mini-skirt in cold weather can be cystitis, and not only cystitis, but chronic recurrent and even inflammation of the appendages, which threatens with many years of medical procedures, infertility and hopes for recovery.
- Please note that frequent acute respiratory infections and acute respiratory viral infections indicate a decrease in the functions of the immune system and measures should be taken to improve its condition.
- Try not to hold your urine when you want to urinate, otherwise holding your urine will lead to a bladder infection.
- Adhere to a normal drinking regime - 2 liters of water per day, and in the heat - 1-1. 5 liters more.
- Women are advised to use tampons, not tampons, which can compress the urethra and become a source of infection, and hence the bladder.
- Men are advised to change their underwear daily, which will protect as much as possible from the occurrence of non-specific urethritis.
- When using the toilet, it is recommended to wipe from front to back, not the other way around, to avoid bringing intestinal bacteria into the external genitalia, where they can enter the urethra and bladder.
Following these tips will not be able to get rid of cystitis 100%, but will help to minimize the risk of disease.




























